The central processing unit (CPU) is the brain of a computer. The CPU’s instructions are used by all of the system’s primary components, including the graphics card and RAM. As a result, a properly working processor is an essential component of any gaming PC.
When a game stutters or crashes, open applications stop responding to new inputs or programs open slowly, excessive CPU consumption may be the culprit.
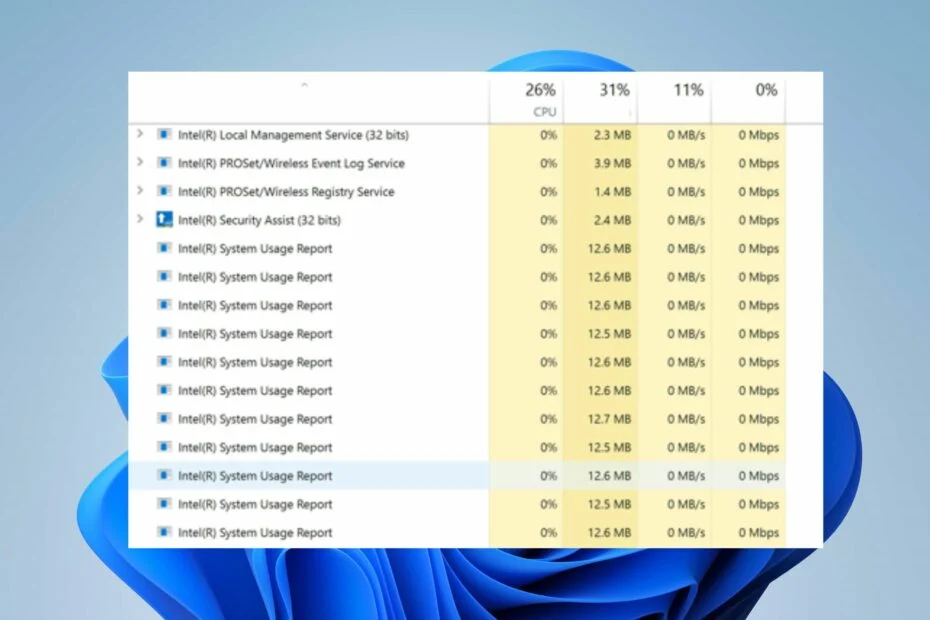
Users complain about the high CPU utilization of the Intel System Usage Report on their PCs, which affects performance. The utility tool consumes an excessive amount of CPU power, leaving insufficient power for other programs on the PC. While playing games, the computer began to crash regularly. So, what exactly is the Intel System Usage Report, and do you need it on your computer?
Following an initial investigation, the computer was found to be substantially laden with Intel System Usage Report activities. Let’s go over how to fix high CPU utilization in Windows 10*.
Recommended Post:- How to Download HDMI Video Drivers on Windows 10
What exactly is the Intel System Usage Report
The Intel System Usage Report is one of the Intel Driver Update Utility’s operations (now the Intel Driver & Support Assistant). The Intel Driver Update Utility (now known as the Intel Driver & Support Assistant) is Intel’s driver download and update application.
Intel System Usage Report is a mechanism that sends telemetry data to Intel servers for analysis and improvement of CPU performance. You may also send such data if you utilize an Intel processor.
High CPU load is reported by Intel System Usage.
In my friend’s situation, the CPU was high since the Intel System Usage Report wasn’t working properly, and there were many processes with that name.
As I continued to look for answers, I learned that this was not a unique incidence, but rather a rather widespread issue with the Intel Usage Report. For some, the problem was caused by a loaded CPU, whereas for others, it was caused by a loaded RAM. As a result, rather than waiting a lengthy time, we opted to eliminate the program that was causing this procedure.
And, yes, the machine would continue to run in the old performance mode after deleting the software.
As a result, if you are having a similar problem, we recommend that you uninstall the Intel Driver Update Utility (now the Intel Driver & Support Assistant). This program is not required for your computer, so proceed with caution.
Is it safe to turn off the Intel System Usage Report?
SurSvc.exe is a process of the Intel Driver Update Utility, which is currently known as the Intel Driver & Support Assistant. Its functions are as follows:
- It has nothing to do with the computer and is used to send telemetry reports to Intel regularly. It is also commonly deployed alongside the Intel Driver Update Utility.
- Intel analyses data from the Intel System Usage Report to optimize CPU utilization. Unfortunately, the process causes CPU utilization concerns because it will not cease operating in the background, resulting in high CPU usage.
Disabling Intel System Utilization Report on your PC, on the other hand, can assist you to get around its CPU and cause high RAM usage.
It is safe to disable it because the process has no bearing on the performance of your computer. SurSvc.exe is located in a subdirectory of C: Program Files on your computer.
How can You repair the Intel System Usage Report when You have a powerful CPU?
Before starting with any problem-solving measures, review the following:
- Turn off any background apps that are running on your computer.
- Unnecessary apps should be closed.
- Restart Windows in Safe Mode and see if the excessive CPU consumption in the Intel System Usage Report persists.
If the high CPU utilization persists, implement the solutions listed below.
Solution 1: Run a Clean Boot
- Step 1: Open the Run dialogue box by pressing Windows + R, then type MSConfig and click OK.
- Step 2: Go to the Services tab and click the Hide all option. Step 3: Select Microsoft services, then click the Disable all button.
- Step 4: Select the Startup tab and then click Open Task Manager.
- Step 5: Select the startup programs and then click the Disable button.
- Step 6: Restart your computer to see whether the excessive CPU utilization persists.
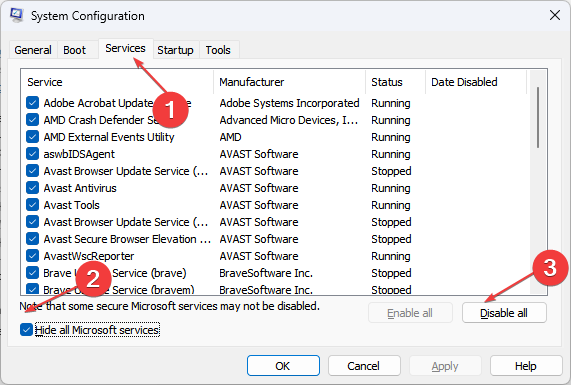
A clean boot prevents third-party apps from launching from the start. It prohibits any starting procedure from interfering with the Intel System Usage Report processes.
Solution 2: Turn off the Intel System Usage Report.
- Step 1: To launch the Windows Services manager, press Windows + R to open the Run dialogue box and type services. MSC, and click OK.
- Step 2: Select the Intel System Usage Report from the list of services.
- Step 3: Right-click it and choose Properties from the drop-down menu.
- Step 4: Finally, set the Startup type to Disabled.
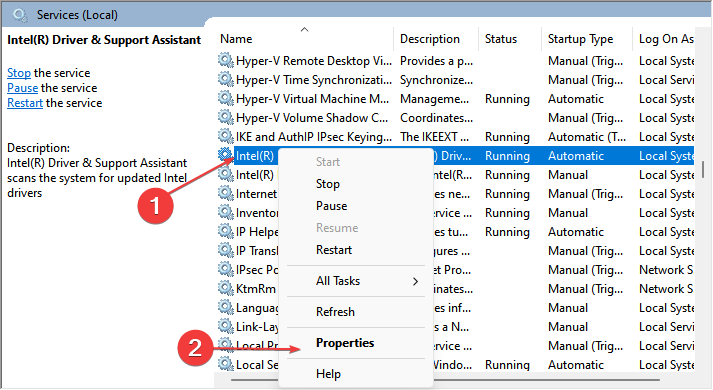
Disabling the Intel System Usage Report service will prevent it from utilizing your CPU or memory space.
Solution 3: Remove the Intel System Usage Report from your computer.
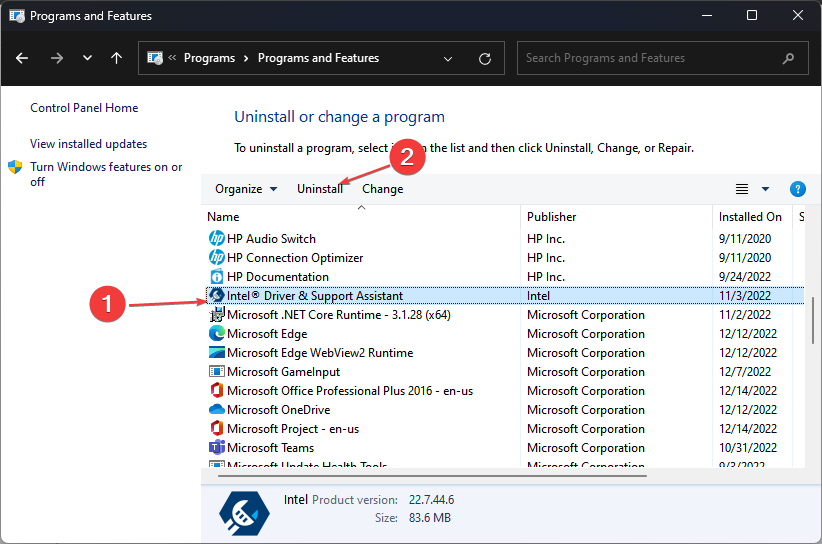
- Step 1: To open it, left-click the Start button, type Control Panel, and press OK.
- Step 2: Select Programs and Features.
- Step 3: Locate the Intel System Usage Report or the Intel Driver & Support Assistant, right-click it, and choose Uninstall from the drop-down menu.
- Step 4: To finish the installation, follow the on-screen directions.
- Step 5: Restart your computer to see if the Intel Driver & Support Assistant is still available.
Solution 4: Use a third-party uninstaller
There are several application uninstallers accessible online that you may download and install on your PC to delete difficult-to-uninstall software.
If you are having trouble deleting the Intel Driver & Support Assistant from your PC, we recommend that you install one.
Solution 5: Check for Malware
If the problem persists, it could be caused by malware masquerading as a normal Windows process. Some malicious apps consume up CPU and GPU bandwidth for different purposes (for example, mining bitcoin) while showing in Task Manager under a familiar name like “Cortana.exe” or “Runtime Broker”.
To check for this, run a complete scan with your preferred virus application. One decent option is the free offline security scan provided by Windows Security (which runs in your taskbar or Windows settings).
Solution 6: Windows Reinstallation
If you have a restore point from before your CPU problems started, consider utilizing it. However, because Windows disables System Protection by default, most of us do not.
In that situation, reinstalling Windows may be your last option. This can be a time-consuming process, but it can alleviate CPU use concerns caused by software.
“Reset this PC” in Windows 10 will delete all of your programs but leave your personal files alone. You’ll then have to reinstall all of your non-Windows programs, and your settings will be lost unless you save and back them up. Back up all of your personal files as well, either on an external disc or through cloud storage services, just in case.
When you’re ready, click the Start button and type “Reset this PC” into the search box. Then press the “Get Started” button.
The procedure could take an hour or more. When it is finished, you will need to reinstall your programs.
Solution 7: Additional Programs
CPU-Z is a trustworthy program for examining general information about your CPU and motherboard. After you install and open it, you’ll see the specific model numbers of your CPU and motherboard, as well as some performance data. Use those model numbers to look for support threads about CPU utilization online.
Task Manager isn’t the sole tool for monitoring background processes. Not only does Process Monitor track CPU consumption, but it also logs registry, file system, and network activity. If you believe a process is malware, use this program to monitor network activity.
Performance Monitor, a built-in Windows utility, provides a more thorough picture of a process’s CPU consumption over time. To access it, use Windows Key + R and then type “perfmon”.
Performance Monitor contains far too many complex features to list here, but in summary, it allows you to easily divide CPU utilization into different categories per task and track it over time for advanced troubleshooting.
Solution 8: More Techniques to Boost Your CPU
CPUs are built to operate securely at 100% CPU use. However, you should avoid these scenarios anytime they cause noticeable lag in games. The instructions above should teach you how to fix excessive CPU utilization and, hopefully, eliminate the issues that are causing your CPU usage and gaming to suffer.
Unfortunately, not all CPU problems can be resolved with software remedies. If your CPU can’t keep up with the games or programs you’re asking it to run, it’s time to upgrade. The most recent Intel® CPUs provide performance gains for multitaskers and gamers looking to improve their game. To see what upgrades are available, look at the feature sets for the current Intel gaming laptop and gaming desktop CPUs.
Solution 9: Online, you can find specific guidance.
High CPU utilization can be caused by a variety of processes, and there is no one-size-fits-all solution. To discover particular guidance, acquire the name of the process from Task Manager’s Processes or Details (a more specific view), then search online for support forums on the subject.
If your initial query yields no results, include any further information that may be useful, such as the model of your processor (listed next to “Processor” in System Information) and the names of any other programs that appear to be causing the problem. It’s difficult to uncover a bug that hasn’t already been mentioned in hardware and gaming communities, so take the time to experiment with different search terms.
Solution 10: Updating Drivers
If a process continues to consume too much CPU, try updating your drivers. Drivers are programs that manage specific devices that are attached to your motherboard. Updating your drivers may resolve compatibility issues or faults that are causing excessive CPU consumption.
Select Settings from the Start menu. Then, under Updates & Security, click the “Check for Updates” option. This will bring crucial drivers up to date. Graphics card manufacturers also offer programs (such as NVIDIA GeForce Experience for GPUs) that may increase overall game performance.
Some uncommon issues may be resolved by changing your BIOS version. The BIOS (Basic Input Output System) is firmware stored on the motherboard that sends startup instructions to the computer’s other components. Because updating the BIOS rarely results in performance gains (and sometimes introduces new problems), only do so if you’ve identified the defect causing excessive CPU utilization and discovered a BIOS update that directly resolves it.
Solution 11: Reboot
The first step is to save your work and restart your computer. For a reason, “turn it off and on again” is standard troubleshooting advice. This may cure the problem, especially if you haven’t restarted in a long time – a reboot can clear up temporary files and potentially resolve delays in long-running programs.
Solution 12: Power Options
Some power settings, whether on a laptop or a desktop, can reduce the speed of your CPU. By going to the start menu and typing “Edit Power Plan,” you may check your Power Options. Once the window is open, click “Power Options” in the address bar at the top of the screen. Click “Show additional plans,” then select a plan that is not a power saver. Reopen Task Manager to determine if CPU utilization has returned to normal.
Conclusion
The Intel System Usage Report is a feature of the Intel Driver Update Utility (formerly known as the Intel Driver & Support Assistant) that merely sends data to Intel servers. As a result, if you suspect that this procedure is slowing down your computer, simply uninstall it.